About The Conference
The 2018 Innovations in Industry Technical Conference aims at showcasing new technology being implemented in our industry, demystifying these new technologies as well as allowing our Presenters to detail how they have harnessed these new technologies to improve and enhance their current outputs.

This Conference hopes to showcase local initiatives in some of these areas above in order to show that they are no longer pie-in-the-sky technologies, but real-world and applicable, being actively deployed in current operational scenarios by our own local industry.
Our Presenters, all innovative pioneers in their own fields, will unveil the mystery, will detail their applications, explain their experiences, both good and bad, and hopefully broaden your horizons to what is possible if these exciting technologies are embraced and focused to your own operational needs.
At the very least, this Technical Conference will hopefully expose you to these fascinating new technologies and how they could possibly be leveraged in your own fields...
At the very best, it will spark in you a curious and creative urge to do much further investigation yourself, to contact and network with our Presenters, to try and apply them to your current applications, and together to drive our local industrial effort forward into the future...
More Reading...
The world as we know it has irrevocably changed in the last decade, and has been driven by a rapid and accelerating technological revolution with new technological marvels being announced on a virtually daily basis.
We have become almost blase about the fact that we can source virtually any information and communicate with anyone across the world using a small device that fits into our pockets...previously the domain of only Sci-Fi movies.
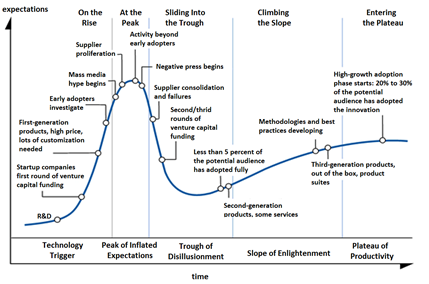 The Gartner Hype Cycle depicts actual advancement of an emerging technology as reaching maturity once it enters what they term the Plateau of Productivity, representing the expectations of the technology finally being absorbed into use in everyday life or being taken onboard in the industrial mainstream.
The Gartner Hype Cycle depicts actual advancement of an emerging technology as reaching maturity once it enters what they term the Plateau of Productivity, representing the expectations of the technology finally being absorbed into use in everyday life or being taken onboard in the industrial mainstream.
In the very recent past, there has been an acceleration of specific technologies, above and beyond niche or personal applications, that have begun to be adopted across the board as being new technology trends that are expected to not only take root, but drive industry forward through the next decade and beyond.
These new and emerging technologies include:
-
the Industrial Internet of Things (iIoT),
the recent convergence of IT and OT has lead to the acceptance and adoption of all items considered part of the Industrial Internet of Things (iIoT) - this is accelerating at a rapid rate across global industry, informing strategic manufacturing decisions that relate directly to operational optimization and direct cost-savings.

"...by 2019, 15 percent of manufacturers who manage data-intensive production and supply chain processes will be leveraging cloud-based execution models with edge analytics for real-time visibility and operational flexibility."
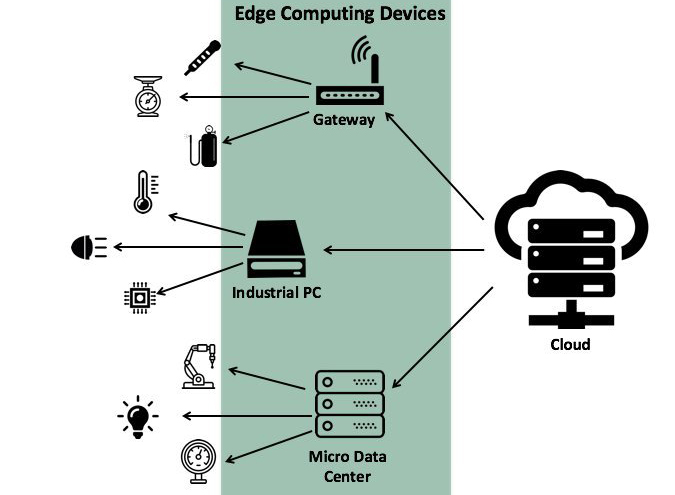 Simplified Edge infrastructures, the movement of intelligence and analytics to the edge have become critical for success for fast visibiity into the manufacturing process.
Simplified Edge infrastructures, the movement of intelligence and analytics to the edge have become critical for success for fast visibiity into the manufacturing process.
The management and monitoring of edge asset performance is a necessity to optimize production, intelligently schedule maintenance and thus also reducing downtime, and this has driven the deployment of Edge Computing and Edge Intelligence.
This further enables quick identification of production inefficiencies, as well as quality, safety and environmental issues in virtual real-time, which slots neatly into the scope of Industry 4.0.
-
Generative Design & Lightweighting,
Lightweighting has become an urgent quest for all global industry, particularly in the aerospace and automotive sectors in order to continually improve fuel efficiency and performance goals. This not only has seen the opening of horizons into use of exotic and lighter materials, but has also recently seen a significant shift in the approach and mindset to Engineering Design.
Gone are the days when designs weren't manufacturable; the rocketing progress of Additive Manufacturing has seen the Design Engineer's imagination set free. Generative Design has enabled the generation of structural components that are beyond the limitations of the old 'first-guess-blocky' conceptual designs, and has also brought Simulation and Analysis right into the Conceptual Phase of the design rather than at the end, where the damage of the olde-worlde guesswork has already long been done.
Generative Design has resulted in amazing tools available to the Design Engineer, enabling a right-first-time option to be generated which is not only incredibly lightweight, but will also check all the boxes iro strength and compliance, and can be quickly produced in multiple material formats via sophisticated AM printers.

-
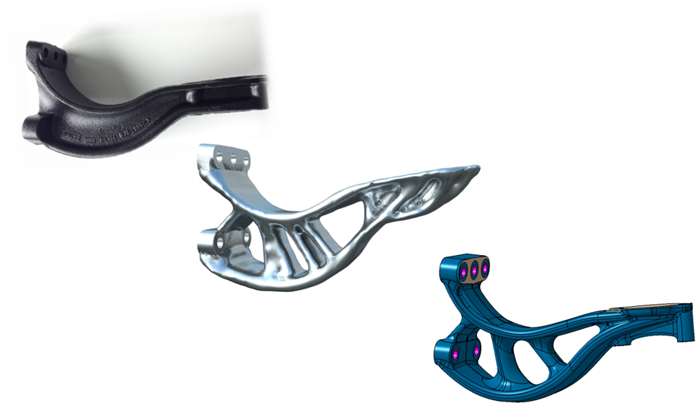
Metal Additive Manufacturing (AM),
3D Printing or Additive Manufacturing (AM) has been around for a while now, and there's hardly an operation that doesn't have a dinky little plastic 3D-printer sitting in a corner of some office. However, the limitations of the traditional plastic 3D Printers quickly became obvious to all who have regretted that purchase.
Metal AM is a game changer though, as components that would have been impossible to manufacture just a few years ago can now be made to exacting standards using a range of metal powders, whilst also enabling the reduction of number of component parts through previous procedures.
No more just a prototyping technology, AM is now increasingly being used for the production of series & bespoke components for the most demanding of applications, as in the remarkable one-piece Bugatti brake caliper depicted below.

-
Augmented, Virtual and Mixed reality (AR/VR/MR) applications in the workplace,
The last two years have seen major advancements in this realm with multiple hardware devices readily available - the very near future will see AR and VR applications of virtually everything, covering design to simulation to maintenance to training to trouble-shooting to marketing and sales.
AR technologies are used to connect the virtual design to real-world physical equipment for operator training, maintenance and visualization, and the potential of the technology at the moments knows no bounds.
Suffice to say, AR in industry is no doubt going to be ubiquitous in a very short timespan...

-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning,
Thanks to IIoT, cloud, big data, and operational analytics; AI-based Machine Learning solutions can be used to make operational changes without the need for programming, utlizing cloud-based dashboards for easy access to a range of analytic options.
Machine Learning makes use of computational statistics and matrhematical optimization to predict defined patterns from data sets, and then utilizes this information to enable increased production capacity, more efficient plant operations, condition monitoring, the optimization of supply chains, and, most importantly, Machine Learning can be leveraged to enable Preventative and Predictive Maintenance.
The integration of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence into automation processes is enabling manufacturers to establish a firm space in the Industry 4.0 revolution.

-
Big Data & Data Analytics,
Data Analytics involves examining and monitoring large data sets from edge assets to uncover hidden patterns, unknown correlations, market trends, customer preferences and other useful manufacturing information.
The Analytics can then lead to more effective condition monitoring, enable more efficient processes, better customer service, improved operational efficiency, competitive advantages over rival organizations and other manufacturing and business benefits.
Big data can then be analyzed with sophisticted software tools & cloud-based dashboards for easy viewing and adaptability as part of advanced analytics disciplines such as predictive analytics, data mining, text analytics and statistical analysis.
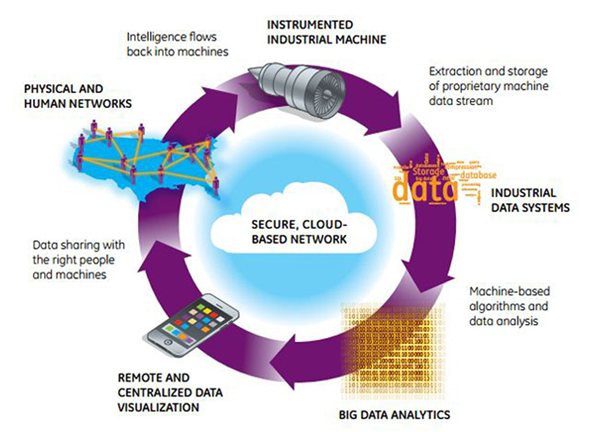
Automated vehicles are increasingly present in modern society, while autonomous applications in the manufacturing plant have been present for some time.
Coupling these with edge intelligence, machine learning and cloud-based Data Analytics expands the capability and control of all autonomous assests already in the plant, and this ties in to the whole upscaling of efficiency across the entire system.

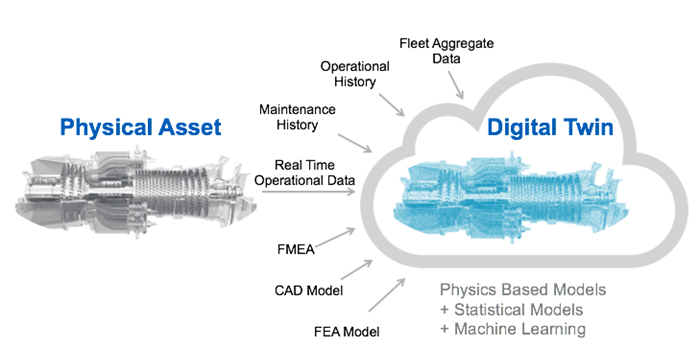
Digital Twin Techniques,
New business models in which virtual services associated with actual products have seen the introduction of Digital Twins, which are virtual replications of as-designed, as-manufactured, and as-maintained physical assets, processes and systems that can be used for various purposes.
These Digital Twins in their virtual representation then provide both the elements and the dynamics of how an Internet of Things (IoT) device operates and lives throughout its life cycle, and are are augmented with real-time condition monitoring and predictive analytics capabilities.
Smart Manufacturing & Transport
Smart Manufacturing is a broad category of manufacturing with the goal of optimizing concept generation, production, and product transaction.
While manufacturing can be defined as the multi-phase process of creating a product out of raw materials, smart manufacturing is a subset that employs computer control and high levels of adaptability.
Smart Manufacturing aims to take advantage of advanced information and manufacturing technologies to enable flexibility in physical processes to address a dynamic and global market.
